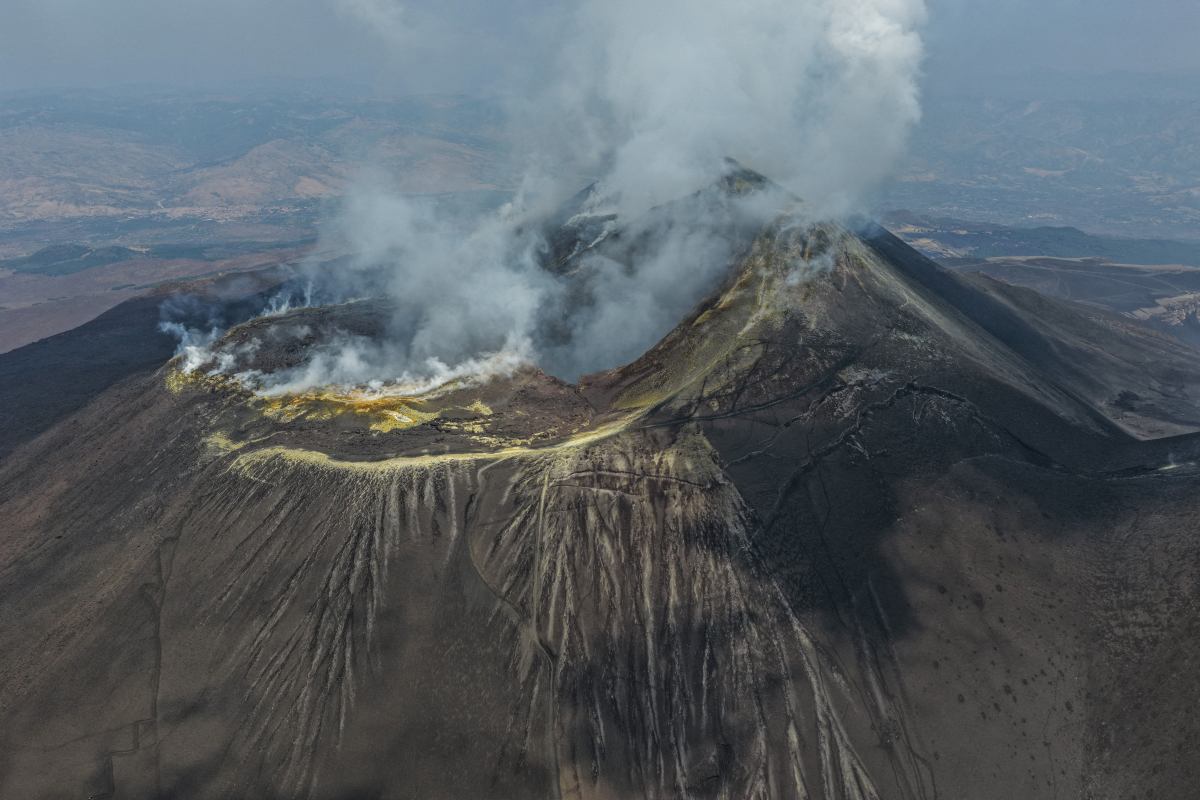
Etna captures expert attention with a fresh fissure, quickly followed by a lava stream.
Etna Makes It Self-Existent
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (INGV) reported a new fissure on the southern flank of Etna, positioned 3,000 m above sea level. Consequently, on Sunday, 10 August, lava began to slowly flow from the volcano. The eruption covered only about 100 m, according to “Il Mondo dei Terremoti,” though activity remained detectable in the southeast crater.
Air Traffic Alert in Catania
The Volcano Observatory System (VONA) issued an orange alert for civil aviation due to the potential intensification of eruptive activity that could threaten flights, especially if volcanic ash were released. No significant emissions were observed during the incident. The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology continues to monitor the situation.
Etna Eruption
The last eruption of Etna occurred on 2 June, with intense activity detected in the southeastern part of the crater. This caused the crater to collapse and produced an eruption plume several kilometers high. According to TG24, the volcanic tremors were very strong. “There is no danger. This is a repeating phenomenon and, based on monitoring, it was already predicted,” said Mayor Enrico Tarantino of Catania in an interview with Adnkronos.
More Information
For more details about Etna, read the article: “Poles lived a moment of fear when the volcano in Europe awakened and showed its power. Chaos ensued” (https://wiadomosci.gazeta.pl/wiadomosci/7,114881,31201326,polacy-przezyli-chwile-grozy-gdy-wulkan-w-europie-przebudzil.html).